Shoulder Arthroscopy in Nagpur
Quick Enquiry
Shoulder Arthroscopy in Nagpur
Shoulder pain can make even simple activities like lifting your arm, combing your hair, or sleeping on one side very difficult. When rest, medicines, and physiotherapy don’t help, shoulder arthroscopy can be a gentle and effective solution.
At Nagpur Arthroscopy & Sports Injury Centre, Dr. Siddharth Jain, an experienced arthroscopy and sports injury specialist, performs shoulder arthroscopy in Nagpur using advanced, minimally invasive techniques. The aim is simple: to help you move freely again, without pain or fear of re-injury.
What Is Shoulder Arthroscopy?
Shoulder arthroscopy is a keyhole procedure that allows the doctor to see and treat the inside of your shoulder joint using a small camera and delicate instruments.
Instead of a significant cut, only a few small incisions are made. This means:
- Less pain after surgery
- Quicker recovery
- Smaller scars
- Faster return to daily activities
This technique is especially useful for people who have sports injuries, wear-and-tear changes, or shoulder instability.
Conditions We Treat With Shoulder Arthroscopy in Nagpur
Rotator Cuff Tears
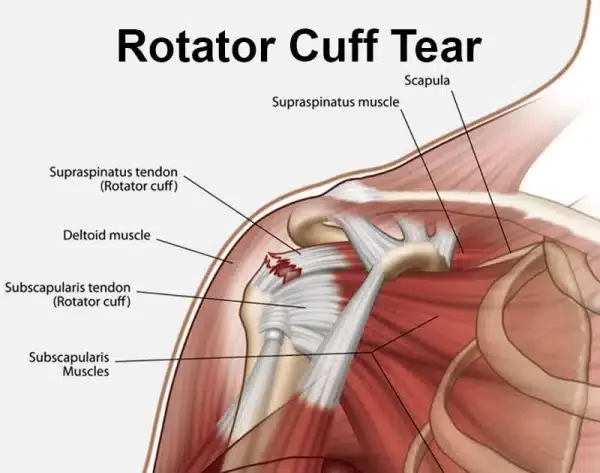
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that help lift and rotate your arm. When torn, it causes pain and weakness, especially at night.
Through arthroscopy, the torn tendon is repaired and reattached to the bone. Patients often notice better strength and sleep within weeks.
Shoulder Impingement Syndrome
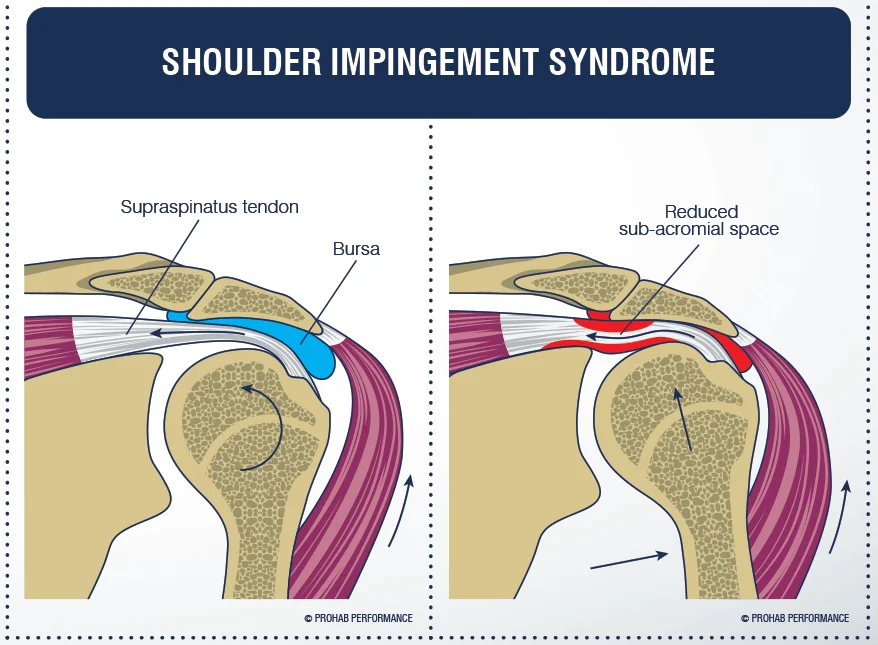
If you feel sharp pain when lifting your arm overhead, you might have impingement. It occurs when soft tissues are pinched between the shoulder blades.
Arthroscopy gently smoothens the bone and removes inflamed tissue, creating more space for the tendons to move freely.
3. Labral Tears and SLAP Lesions
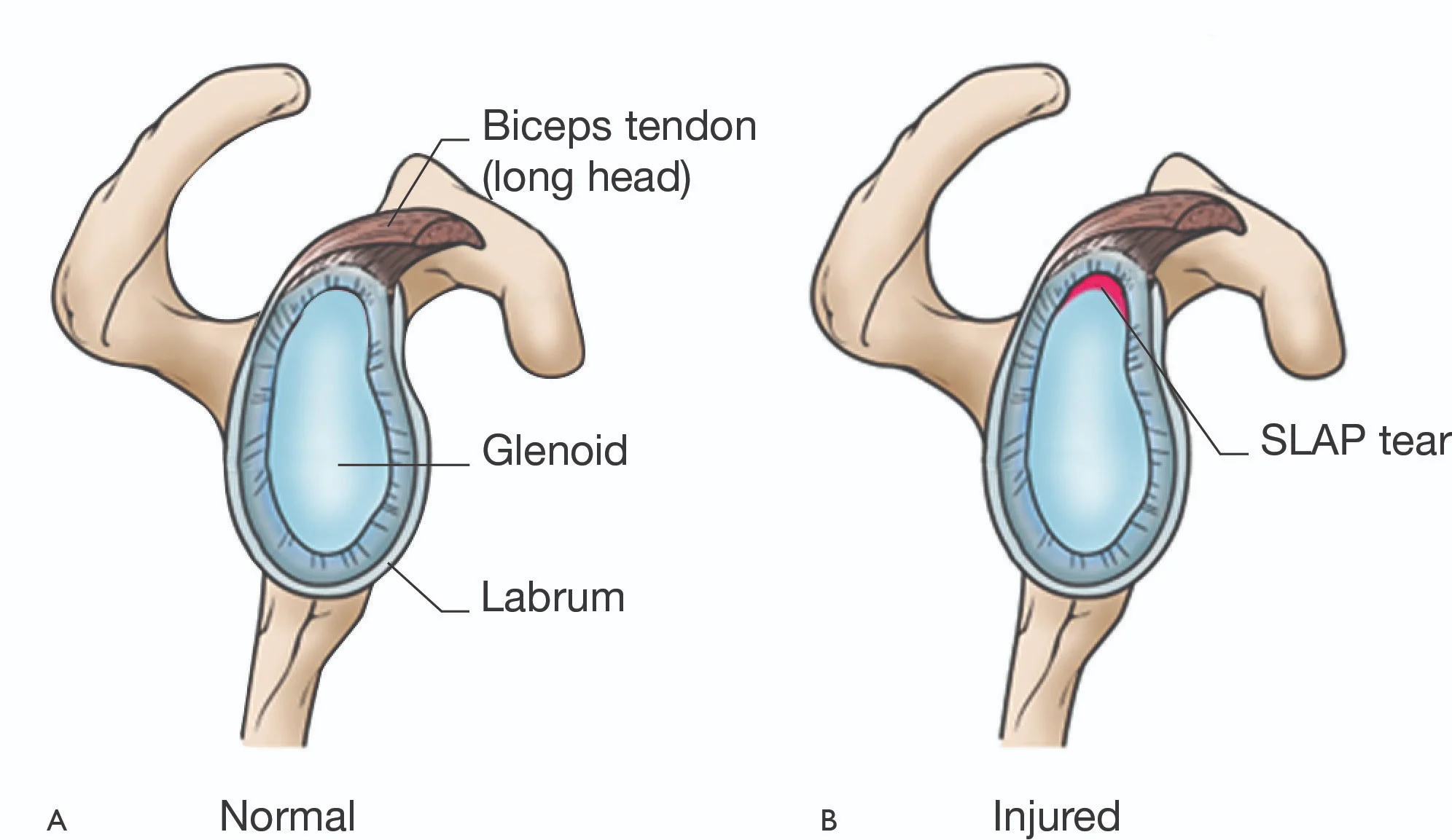
If you feel sharp pain when lifting your arm overhead, you might have impingement. It occurs when soft tissues are pinched between the shoulder blades.
Arthroscopy gently smoothens the bone and removes inflamed tissue, creating more space for the tendons to move freely.
Recurrent Shoulder Dislocation / Instability
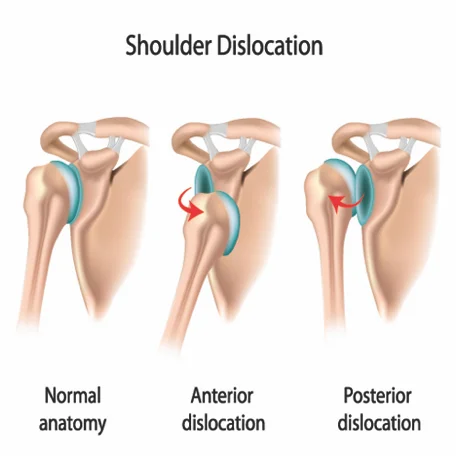
If your shoulder keeps slipping out of place, arthroscopy can help.
The damaged ligaments are tightened and repaired to prevent future dislocations.
This procedure is particularly effective for young sports players who wish to return to activity safely.
Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis)
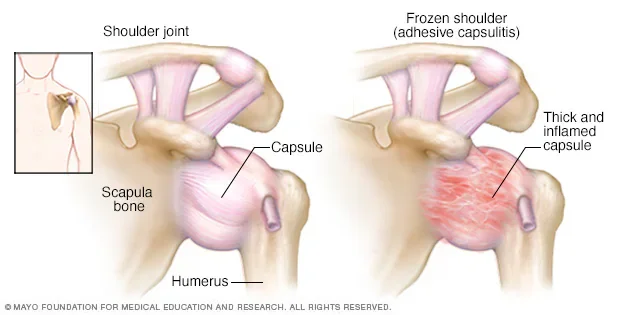
When your shoulder becomes stiff and painful, even daily tasks can feel impossible.
If physiotherapy doesn’t help, arthroscopic capsular release gently frees the tight tissue inside, allowing you to regain motion and reduce pain.
Biceps Tendon Problems
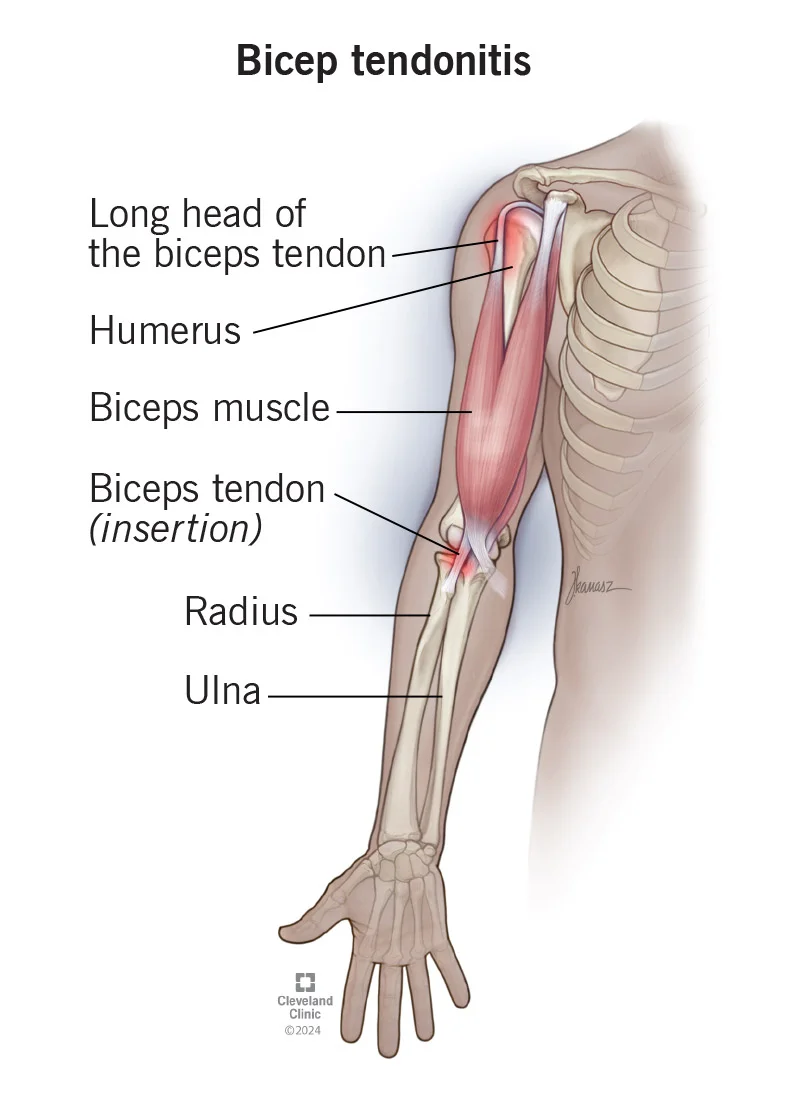
If you experience shoulder pain in the front of your shoulder for 3 to 6 months, it is chronic and could be due to biceps tendon inflammation or a small tear.
Through arthroscopy, the damaged portion is treated or reattached to relieve pain and improve function.
Early Arthritis and Cartilage Wear
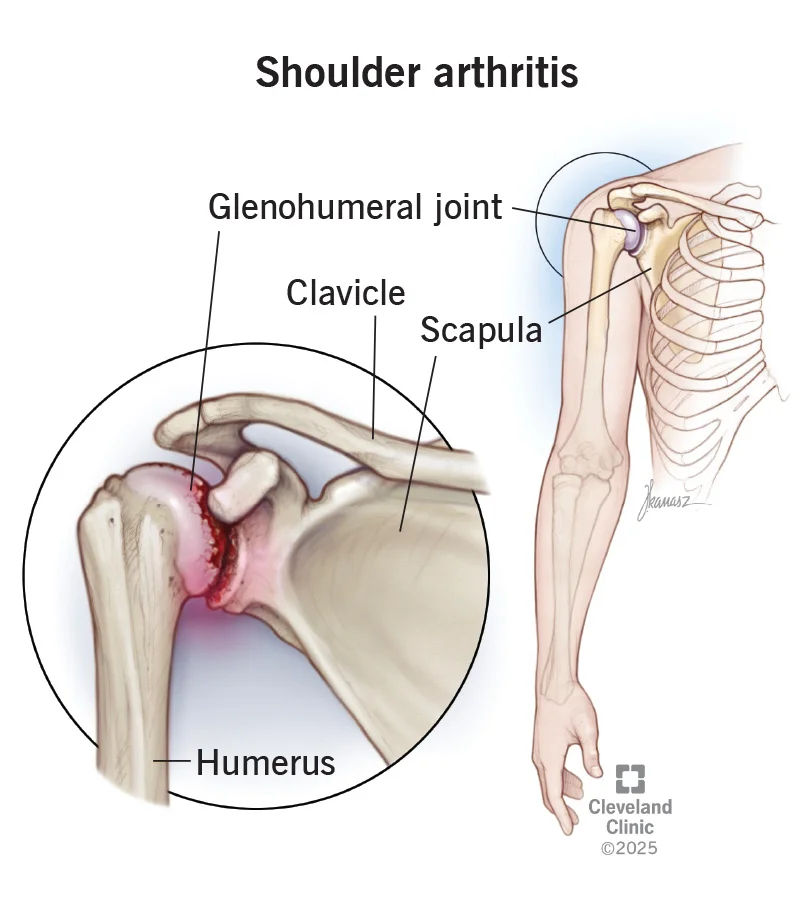
Shoulder arthroscopy can remove loose cartilage, clean the joint, and slow further damage in early stages of arthritis.
It helps reduce pain and improve shoulder movement.
Sports and Traumatic Shoulder Injuries
Athletes and gym-goers often experience shoulder injuries due to overuse or sudden trauma.
Arthroscopy provides precise treatment with minimal downtime, helping patients return to their sport or routine faster.
How We Perform Shoulder Arthroscopy in Nagpur
Pre-operative evaluation
You’ll have a detailed review of symptoms, physical exam, and imaging (X-ray, MRI as needed). We’ll try non-surgical treatment first, where possible.
Day of surgery
Arthroscopy is usually done under regional or general anaesthesia. Small incisions are made for the camera and instruments. The surgeon fixes the problem, for example, reattaching a tendon, trimming inflamed tissue, or repairing a labrum.
Hospital stay & immediate care
Most patients go home the same day or after a brief observation period. You’ll receive pain control instructions and a sling if needed.
Early recovery (first 2–6 weeks)
Gentle range-of-motion exercises are started early to prevent stiffness. Pain usually improves quickly with the right meds and care.
Rehabilitation (6–12+ weeks)
A structured physiotherapy plan helps regain strength and function. Return to daily activities is gradual; sports or heavy labour may take longer depending on the repair.
Timeline (typical)
- Pain reduces within days to weeks.
- Improvement in movement over the weeks.
- Strength and full activity often return in 3–6 months, depending on the injury.
When Should You Consider Shoulder Arthroscopy?
You might benefit from shoulder arthroscopy if you have:
- Shoulder pain lasting more than 3–4 weeks
- Difficulty raising your arm or weakness
- Clicking or catching sensation in the shoulder
- Shoulder dislocation that happens repeatedly
- Stiffness that doesn’t improve with physiotherapy
Early evaluation helps prevent further damage and ensures a faster recovery.
Why Choose Nagpur Arthroscopy & Sports Injury Centre
Expertise you can trust: Dr. Siddharth Jain has completed advanced fellowships in arthroscopy and sports injury from the UK and AIIMS Delhi.
- Modern facilities: Equipped with high-definition arthroscopy systems and dedicated physiotherapy support.
- Personalised care: Every patient receives detailed guidance, from diagnosis to complete rehabilitation.
- Faster recovery: Minimally invasive approach, same-day mobility, and custom recovery plans.
Our focus is always on healing, not just surgery. We help you get back to work, sport, or everyday life quickly without pain.
If shoulder pain is affecting your comfort or confidence, you don’t have to live with it.
Visit Nagpur Arthroscopy & Sports Injury Centre and meet Dr. Siddharth Jain, a trusted shoulder arthroscopy specialist in Nagpur, for an expert opinion and tailored treatment plan.

